We hear more and more the term “Lean Management”. But what exactly is it?
1. Definition of Lean Management
Lean Management is an Anglo-Saxon expression whose main word is evocative. Indeed, the word “Lean” means “no frills”. This echoes the idea of reducing something to the essential, to remove the unnecessary, which is the basis of the Lean method. Lean Management, a term introduced for the first time in 1945 by Toyota, makes it possible to considerably improve the performance of a company, in particular the quality and profitability of production, thanks to the management and organizational methods used. The term was later formalized by an American team of researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). (source)
In short, the goal of Lean is to deliver the maximum customer value in the shortest sustainable lead-time and based on actual demand, while optimising resources, providing the highest possible quality and continuously improving the way you do it (source)
Lean management allows to increase production by optimizing workstations and by eliminating or reducing tasks which are unnecessary or not really having added value. Lean management ultimately has a positive impact, both on employees and on customers thanks to improved satisfaction. (source)
2. A little bit of history
In the 1950s, Lean management appeared in Japan at Toyota. This system was invented by the car manufacturer following the Second World War. The Japanese automotive sector, weakened by the war, no longer had the same weight as the Europeans and Americans. In order to cope with this new reality and rebuild itself, the manufacturer created the “Toyota production system”. This was based on collective intelligence as opposed to the American Taylorist method.
The model was adopted by Westerners in the 1970s and 1990s because they were later faced with the same problems as Toyota. The model was later renamed Lean by MIT. (source)
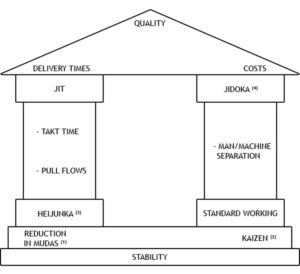
3. The House of Lean
This is a simplified representation of the Lean method. (source) The house of Lean is composed at its base of the two fundamentals to develop the Lean philosophy. Lean requires two conditions to be applied which are:
- The stability of the process
- A working environment reduced to its strict minimum (source)
In order to obtain an orderly work environment, the “5s” and “continuous improvement” tools are regularly used in the Lean precepts.
Once the base is established, andaccording to the maturity of the company, Lean can be deployed through two main axes:
- JIT (or Just-in-time): meet customer demand when there is demand, no more, no less. To achieve this objective, it is necessary to smooth out production in order to standardize its activity.
- Jidoka (also know as autonomation): defect detection. It is a question of being able to determine the potential errors of production at the right time in order to avoid delivering products of low quality or with defects to customers and avoid waste caused by bad production. To reach this objective, the work must be standardized in order to make it mechanical/automatic and as optimized as possible.
The objective to be reached through the Lean philosophy is therefore the equation between costs, quality and delay.
4. The use of lean management in companies
Basic principles have been put in place in order to implement Lean management within companies.(source)
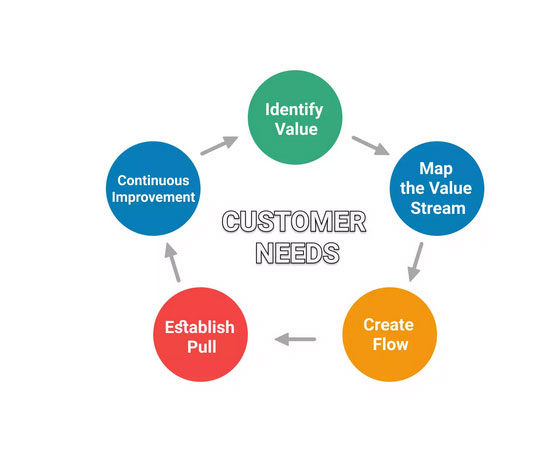
The first step in the implementation of Lean management is to identify the value offered by the company to meet a specific need. It is necessary to identify the activities that will enable the needs to be met and to eliminate superfluous activities that do not contribute to the final value of the product (source).
Then, the second step is to identify the production chain by checking the involvement of each actor. This will allow us to know if the manufacturing process produces value. Thus, it will be possible to remove actions that are repetitive or do not bring any value (source).
The third step is the creation of a fluid work chain. To do this, it is necessary to set up concrete tasks for each actor and remove the problematic points that do not allow the establishment of a fluid production chain (source).
For example, in an industrial environment, it may be necessary to determine specific work areas or locations for specific equipment.
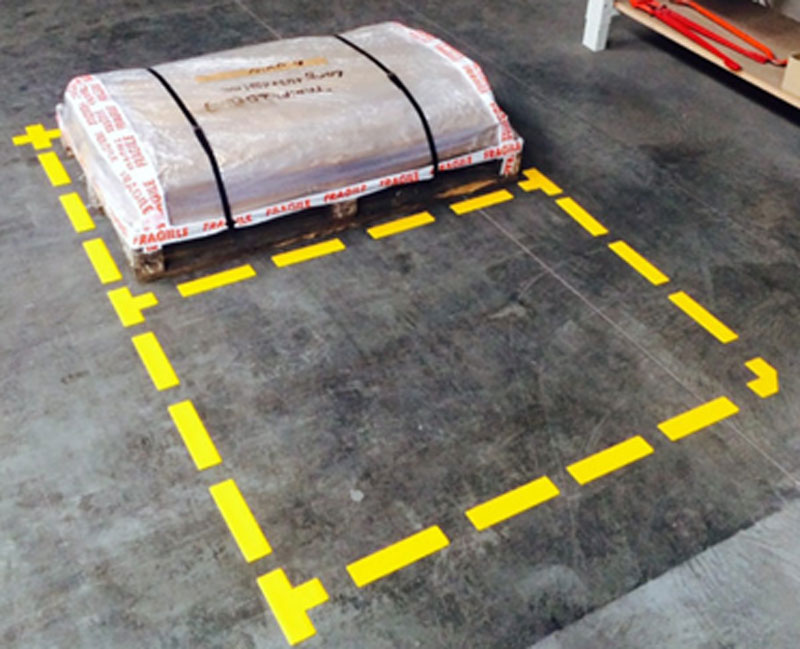

Organizing workspaces is also essential. It is important to remove all cumbersome elements so that the workspace at each workstation is as efficient as possible.

The fourth step is to set up a stable workflow for employees. For example, it is possible to only produce products on demand in order to meet customer needs. This way, it will be possible to optimize the workflow and avoid waste due to unsold products (especially for services such as restaurants) (source).
The last step for the implementation of Lean management in a company is continuous improvement. Each employee can participate in his or her own way in the continuous improvement process by giving ideas for improving products, processes or the way tasks could better be performed (source). The main goal is to optimize as much as possible the tasks that are carried out from A to Z during the manufacturing process of a product.
There are various tools that can be used to set up and improve the manufacturing process. For example, the “5s”, the “Takt Time”, the “added value”, the “non added value” etc.
5. Le Lean Management also at home
Lean management is not exclusively reserved to professionals. In fact, its benefits can be found not only in companies, but also at home. Lean management can allow you to define a storage and organization system for tidying up your home. The primary purpose of this system is to save time. The most concrete place to apply Lean Management is in the kitchen.It is possible to find different ways to store your equipment and utensils in order to easily get your hands on them and optimise your time spent cooking (source). Besides the kitchen, there is the bedroom, the bathroom and of course the home office. But Lean management can be applied everywhere and all the time (source). Thanks to Lean management it is possible to review certain household routines to save time in the morning, for example, to go faster on household tasks at the weekend or to be efficient when working from home. (source)
6. The benefits of Lean Management
Lean management can be found at all hierarchical levels of a company. It takes into account the notion of worklife in the company and working conditions and has a positive impact on both all the while improving productivity and performance.
Indeed, Lean management allows, for example, to improve communication between employees, to optimise workstations and to allow employees to better concentrate on rewarding tasks.
Employee satisfaction is improved due to better working conditions, thus improving the quality of work with a direct impact on customer satisfaction and company growth.
Certainly, Lean reduces waste in production by focusing on core production steps and focusing on the tasks that have value.
By focusing on the activities that create value, employees are more efficient and productive. Thanks to Lean management, they are less distracted by unnecessary and superfluous tasks and therefore more precise in their work.
With activities reduced to the essentials and employees focused on delivering value, Lean management’s aim is to optimise the flow of activity in the company by defining work periods more efficiently. The advantage of Lean management is that it adapts work to the actual demand and thus better manages and uses acompany’s resources.
To conclude, the Lean management method is an essential tool in companies because good Lean management saves time and costs, which in turn improves quality and customer satisfaction.
All employees benefit from the use of this management system which facilitates their work and the management of their workstation.
In addition to the industrial environment, Lean management is a concept to be adopted everywhere, even at home, for a better organization of everyday life. (source)